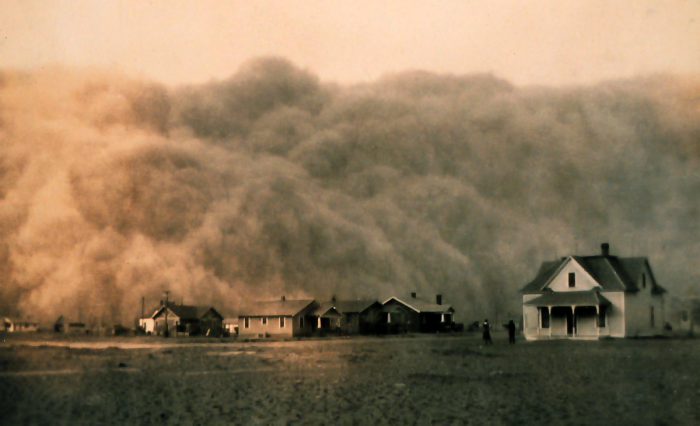
In 1930s, the Dust Bowl occurred and greatly devastated the Midwest. There were four waves of drought that hit North America, spanning from 1930 to 19940. The drought effects were worsened by poor farming methods. Crops were destroyed and soils were left bare. When winds blew, huge clouds of dust were raised, and mounds of dirt covered everything, including houses. The dust caused suffocation in animals and pneumonia in children. This was not all as the storm worsened and the dust was blown to Washington D.C. It worsened the Great Depression and affected land productivity in the United States.
Causes
Weather patterns of the Pacific and Atlantic oceans changed 1930. The changes in weather caused the Atlantic to grow warmer and the Pacific became cooler. As a result, the air current that carries moisture towards the Great Plains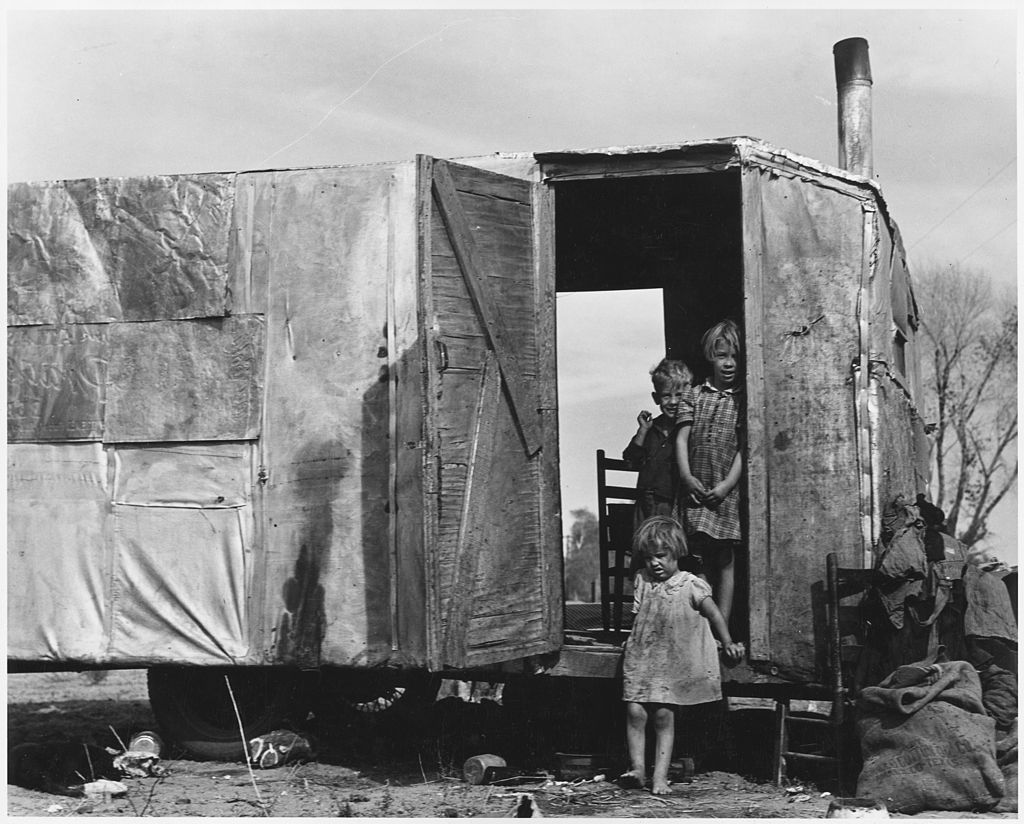  from the Gulf of Mexico changed and the jet stream was weakened and its direction changed. Reaching the Rockies, the current dumped the rains, leading to the creation of tornadoes. The rain failed to reach the Great Plains when the jet stream moved south causing the drought.
from the Gulf of Mexico changed and the jet stream was weakened and its direction changed. Reaching the Rockies, the current dumped the rains, leading to the creation of tornadoes. The rain failed to reach the Great Plains when the jet stream moved south causing the drought.
Besides the change in weather, farmers also contributed to the occurrence of the drought. They cleared the tall prairie grass that covered 5.2 million acres in the Midwest, which used to protect the top soil. Since the land was bare, the remaining top soil was blown away by the strong winds. Parts of Midwest have not yet recovered from the ordeal.
The drought was worsened by the growing dust, which caused the sunlight to be reflected back into space before it could reach the earth. This caused the land to cool since the temperatures dropped. At the end of it all, the less moisture was not enough for the clouds to create enough rains.



 17,000 people succumbed to death as a result of
17,000 people succumbed to death as a result of 
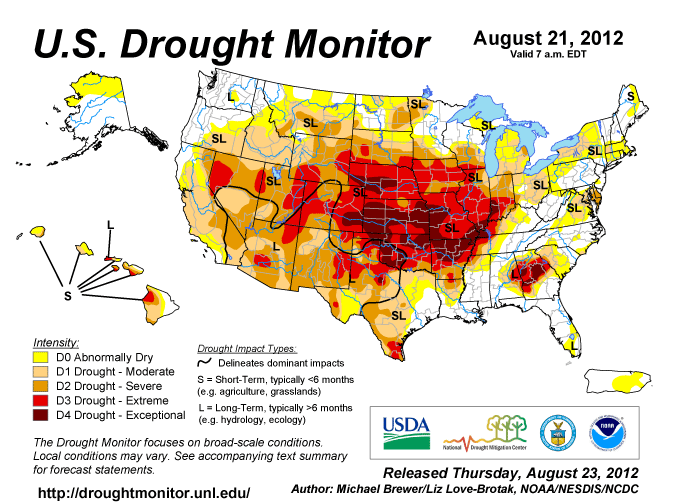 month of March 2012. Drought conditions increased as rainfall decreased.
month of March 2012. Drought conditions increased as rainfall decreased.
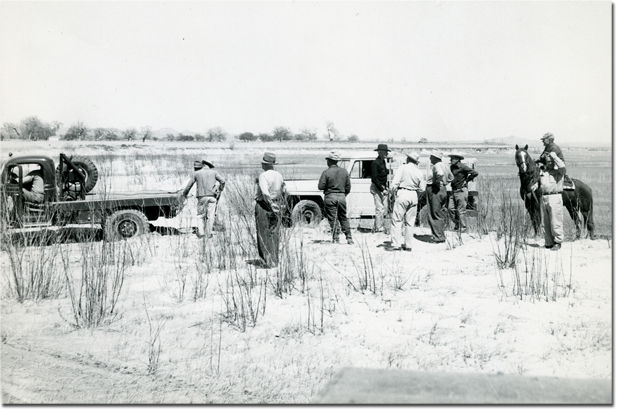
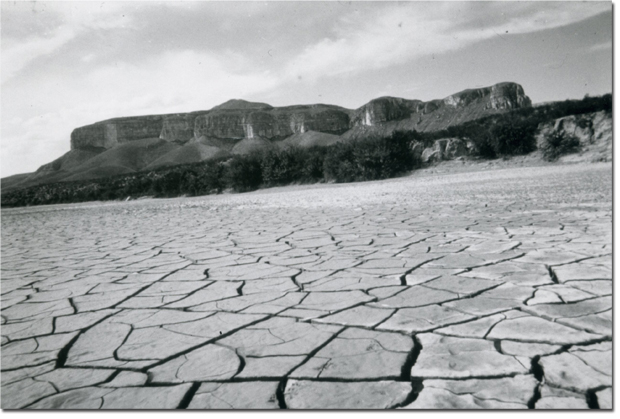
 ts of the drought, in the 1952 summer. Unfortunately, the devastating drought quickly spread to Texas, Oklahoma and Kansas, and the amount of rainfall received was 75% below normal. More than half of Texas received significantly little rainfall. The drought was felt all over, from the Great Plains to the south of New Mexico to Deep South. The Midwest was not spared either. By 1954, a total of 10 states had been affected by the biting drought.
ts of the drought, in the 1952 summer. Unfortunately, the devastating drought quickly spread to Texas, Oklahoma and Kansas, and the amount of rainfall received was 75% below normal. More than half of Texas received significantly little rainfall. The drought was felt all over, from the Great Plains to the south of New Mexico to Deep South. The Midwest was not spared either. By 1954, a total of 10 states had been affected by the biting drought.
 ells, the drought was declared a disaster in some of the affected states, such as
ells, the drought was declared a disaster in some of the affected states, such as